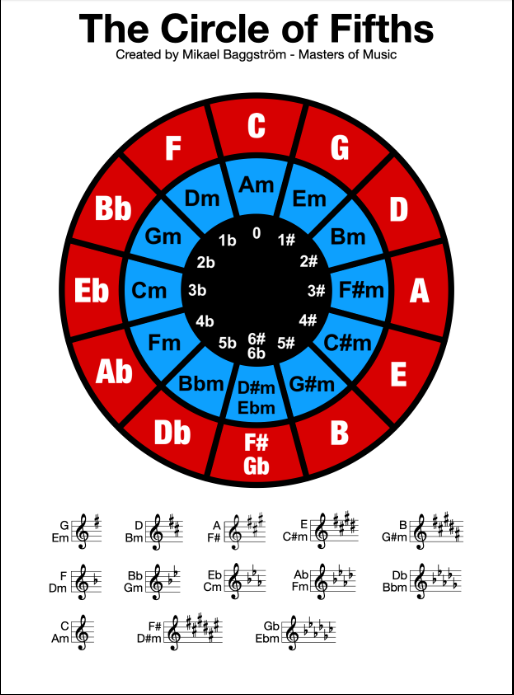
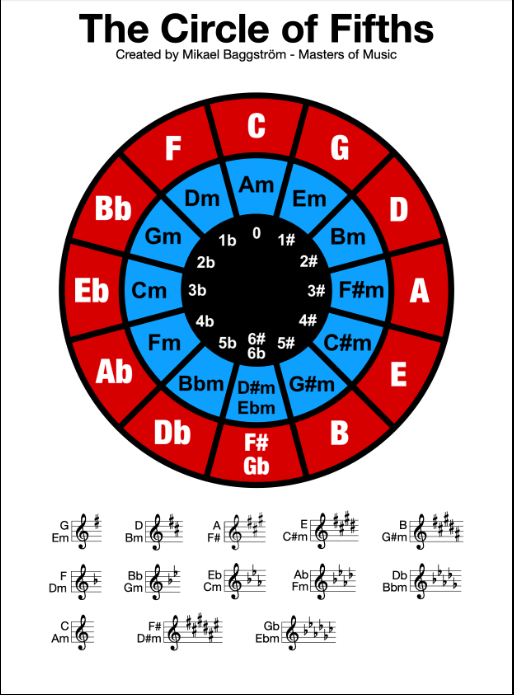
The circle of fifths is a musical tool used to understand the relationship between different musical keys. It is a circular diagram showing the order of the twelve pitches in the chromatic scale, arranged to highlight the relationships between keys.
The circle of fifths is named for the interval of a fifth, which is the distance between two notes that are seven semitones apart. In the circle of fifths, each key is separated from its neighbors by a fifth (or a fourth, depending on the direction you move around the circle).
Starting at the top of the circle, the first key is C major. Moving clockwise, the next key is G major (a fifth above C), D major (a fifth above G), and so on. Moving counterclockwise from C major, the next key is F major (a fourth below C), Bb major (a fourth below F), and so on.
The circle of fifths can also be used to determine the key signatures of different keys. The key signature of a key tells you which notes are sharp or flat in that key. For example, the key of C major has no sharps or flats, while the key of G major has one sharp (F#).
By looking at the circle of fifths, you can see that the key signatures of adjacent keys differ by one sharp or flat. For example, the key of G major has one sharp (F#), while the key of D major has two sharps (F# and C#). The key of A major has three sharps (F#, C#, and G#), and so on.
The circle of fifths is also useful for understanding chord progressions. Chords that are adjacent on the circle of fifths are often used together in progressions. For example, the chords in the key of C major (C, F, and G) are adjacent on the circle of fifths.
In addition to its practical applications, the circle of fifths is also a useful tool for understanding music theory and composition. It can help you understand the relationships between different keys, and it can help you create chord progressions that sound harmonious and satisfying.
In conclusion, the circle of fifths is a powerful tool for musicians and composers. You can create interesting and harmonious music by understanding the relationships between different keys, key signatures, and chord progressions.